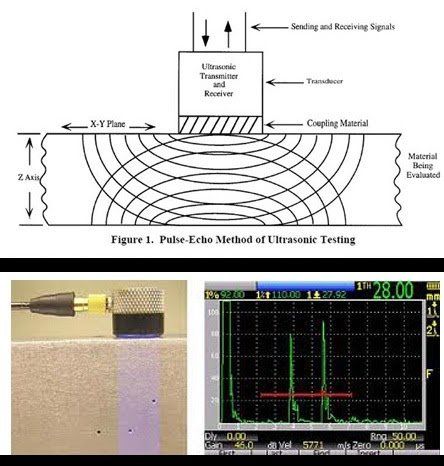
Ultrasonic Testing
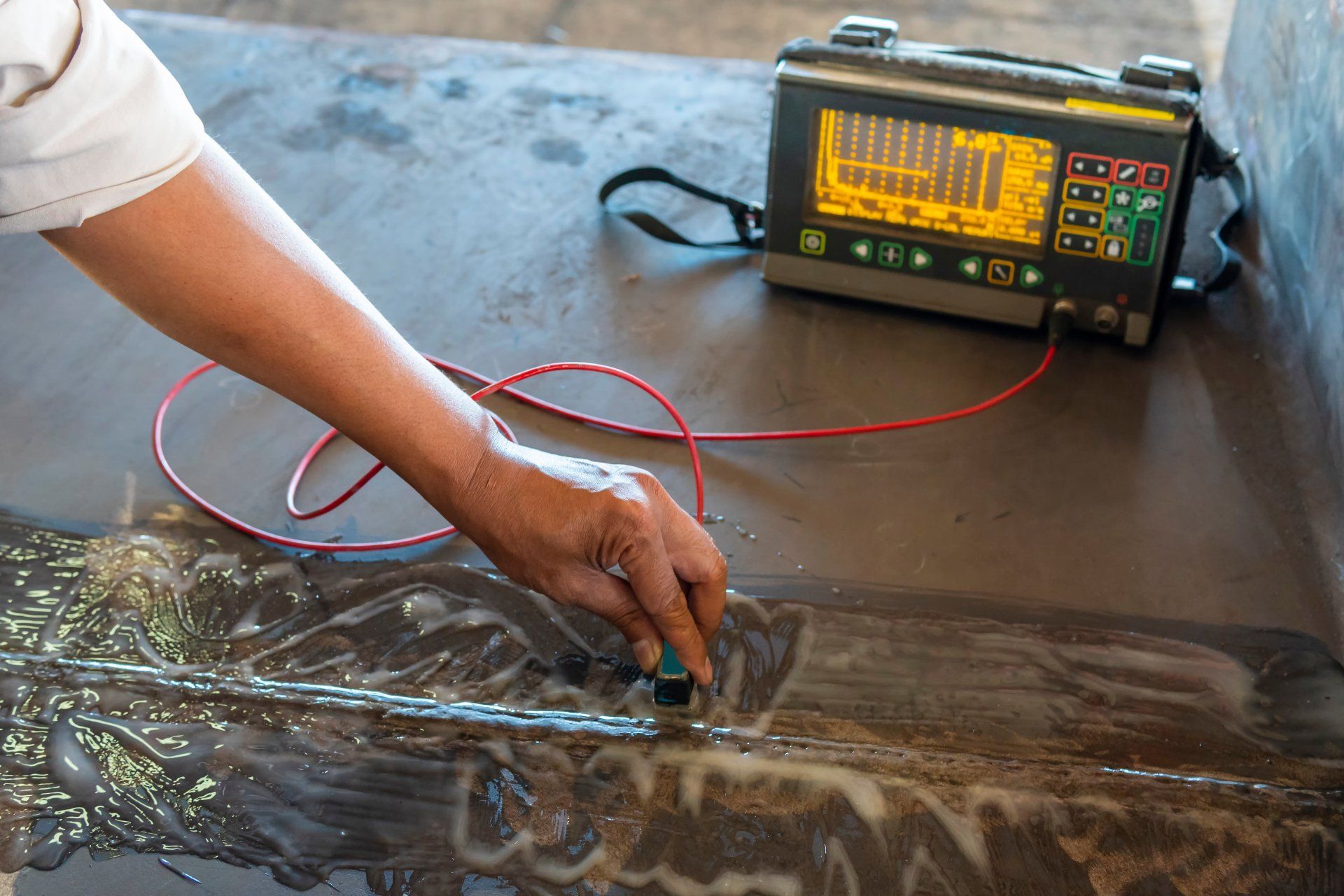
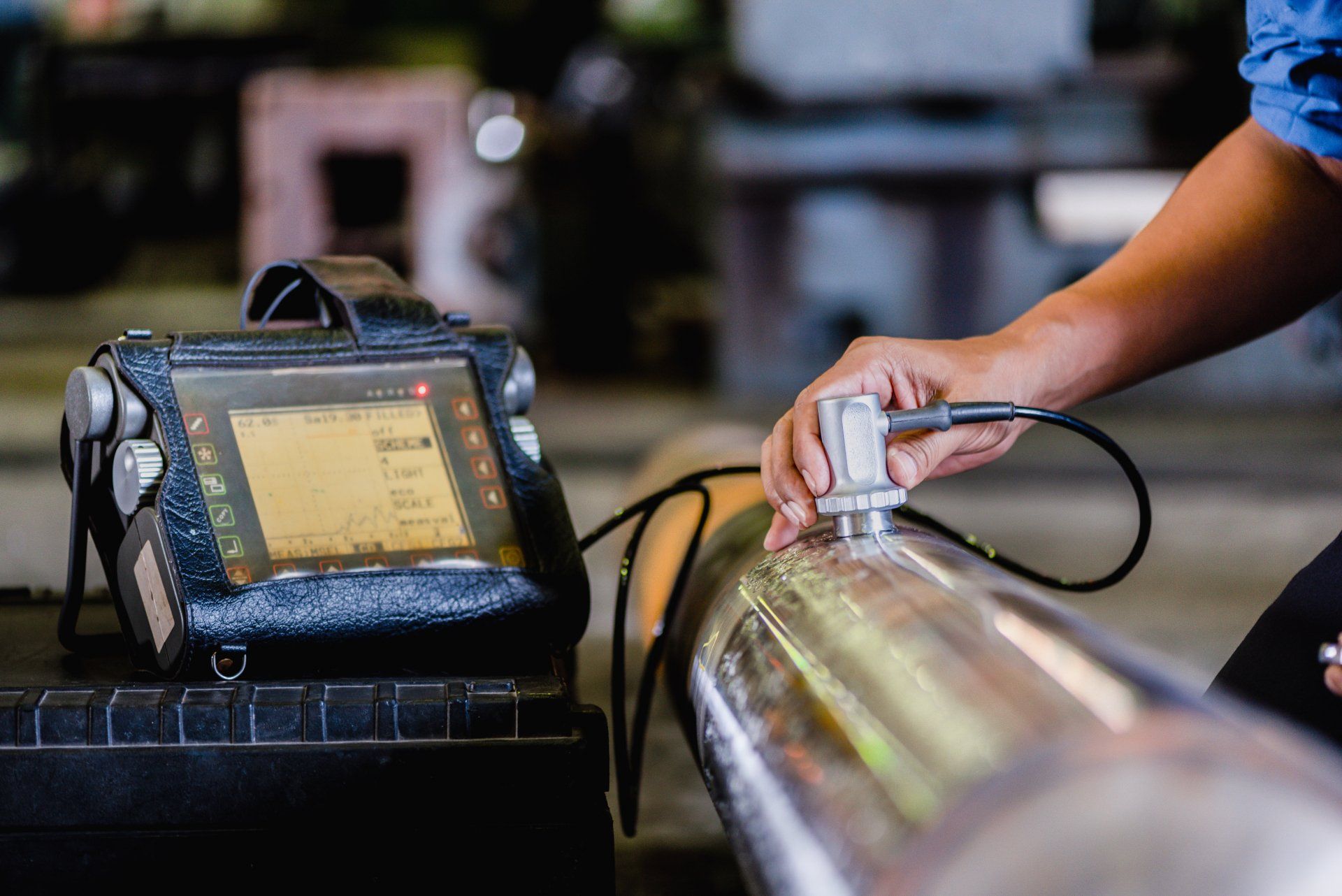
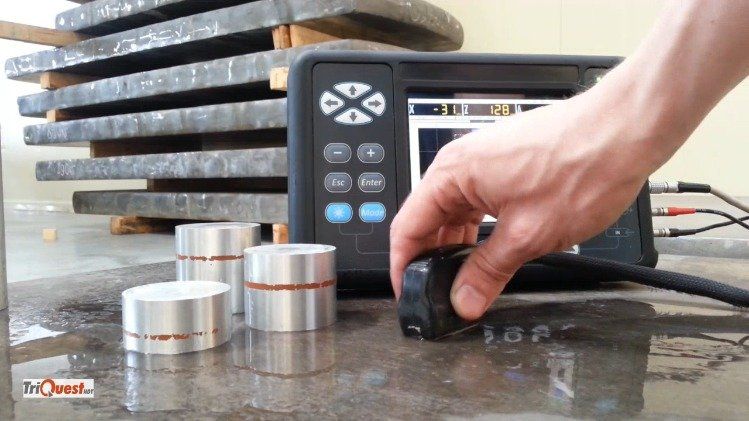
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is an NDT method using high frequency sound energy above the human hearing level of 20 kHz, and is produced by a piezoelectric crystal (transducer) which converts electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, and back to electrical energy for interpretation of the electronic signal. Ultrasonic testing is capable of detecting surface and subsurface defects and/or discontinuities, and is commonly used for measuring material thickness, and for detecting flaws in newly manufactured or in-service components.
Ultrasonic inspection is commonly performed on welds, castings, forgings, pipe, fittings, valves, mechanical shafts, machined parts, pressure vessel category A, B, and D welds, wood, non-metallic materials, concrete, and for the detection of steel plate laminations.
Inspection surfaces must be clean to allow ultrasound transmission between the couplant and the part under examination, and accessibility and immediate obstructions should be minimized particularly when performing shear-wave flaw detection. Thin paint and other coatings are acceptable providing they are not dis-bonded and/or flaking from the area of interest. High temperatures will affect the propagation and attenuation of ultrasound, and therefore, special high temperature transducers and couplants are available for specific applications.