Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD)
Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD)
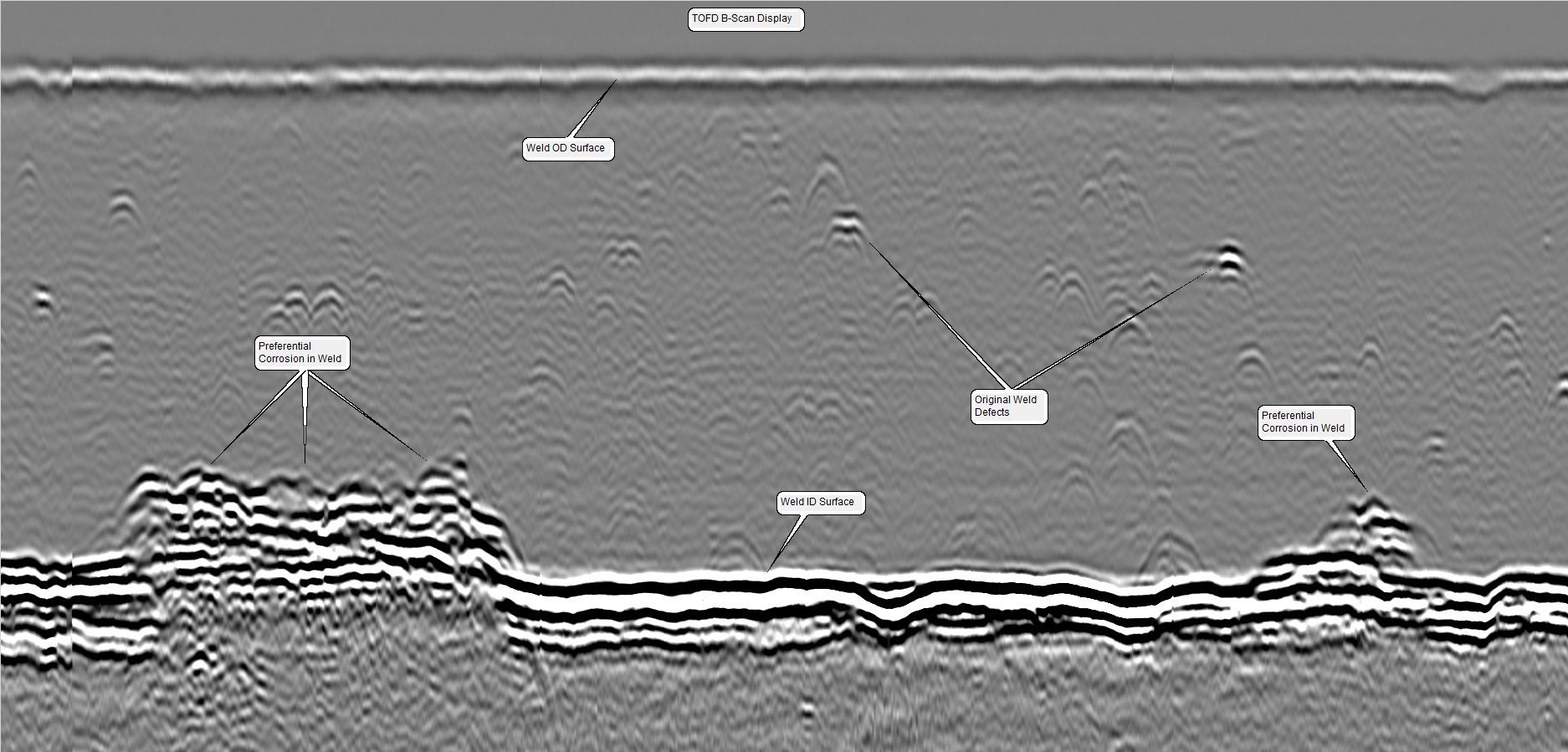
Time of flight diffraction (TOFD) is an ultrasonic method for the detection, sizing and monitoring of flaws in new construction and in-service welds and components.
TOFD employs two longitudinal wave (L-wave) angle beam transducers arranged diametrically on opposite sides straddling the weld or base material under examination. One transducer acts as a transmitter of ultrasonic energy, while the other receives the returning signals. The transducer, pulse, and amplifier characteristics are selected to generate a broad distribution of energy allowing for full weld coverage with single scans. An electronic encoder records the position of the probe along the weld during the scan which enables a real-time display and recording of the digital images.
Defect detection is identified when there is a diffraction of the ultrasonic wave from the tip(s) of the defect(s). Measurement of the time of flight of the pulse allows the depth of a defect tip to be calculated using the TOFD technique. This allows the NDT technician to size the indications to determine acceptance or rejection per the applicable code and/or client specification.
TOFD is often complimented by using other ultrasonic conventional and/or phased-array (PAUT) methods